DNS Failover with Route53
DNS Failover with Route53

Route 53‘s DNS Failover feature gives you the power to monitor your website and automatically route your visitors to a backup site if the main target is not healthy. To showcase this feature, we are going to deploy an application, which we built in this blog post, to two different AWS regions. We are also going to set active-passive failover in Route53, then we will remove the application from one region and we’ll observe how DNS queries will react to the changes.
AWS describes the failover scenarios in 3 different categories
Active-passive: Route 53 actively returns a primary resource. In case of failure, Route 53 returns the backup resource. Configured using a failover policy.
Active-active: Route 53 actively returns more than one resource. In case of failure, Route 53 fails back to the healthy resource. Configured using any routing policy besides failover.
Combination: Multiple routing policies (such as latency-based, weighted, etc.) are combined into a tree to configure more complex DNS failover.
Follow this blog post and deploy the example stack to two different AWS regions, for this example we will use us-east-1 and us-west-1 regions. To not interfere with CDK state, I would encourage our readers to copy provided CDK example to two different folders.
Deploy the first stack to us-west-1 region
AWS_REGION="us-east-1" cdk deploy
Deploy the second stack to us-east-1 region
AWS_REGION=”us-west-1" cdk deploy
After successful deployments, you should have two load balancers ready for serving requests
EcsGo-Farga-25T9JCLD3XMK-1007273806.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com
EcsGo-Farga-1PJH0G7U7G8DA-1685310413.us-west-1.elb.amazonaws.com
Head over to the Route53 console next.
Set the primary record with the ALB in us-east-1 region
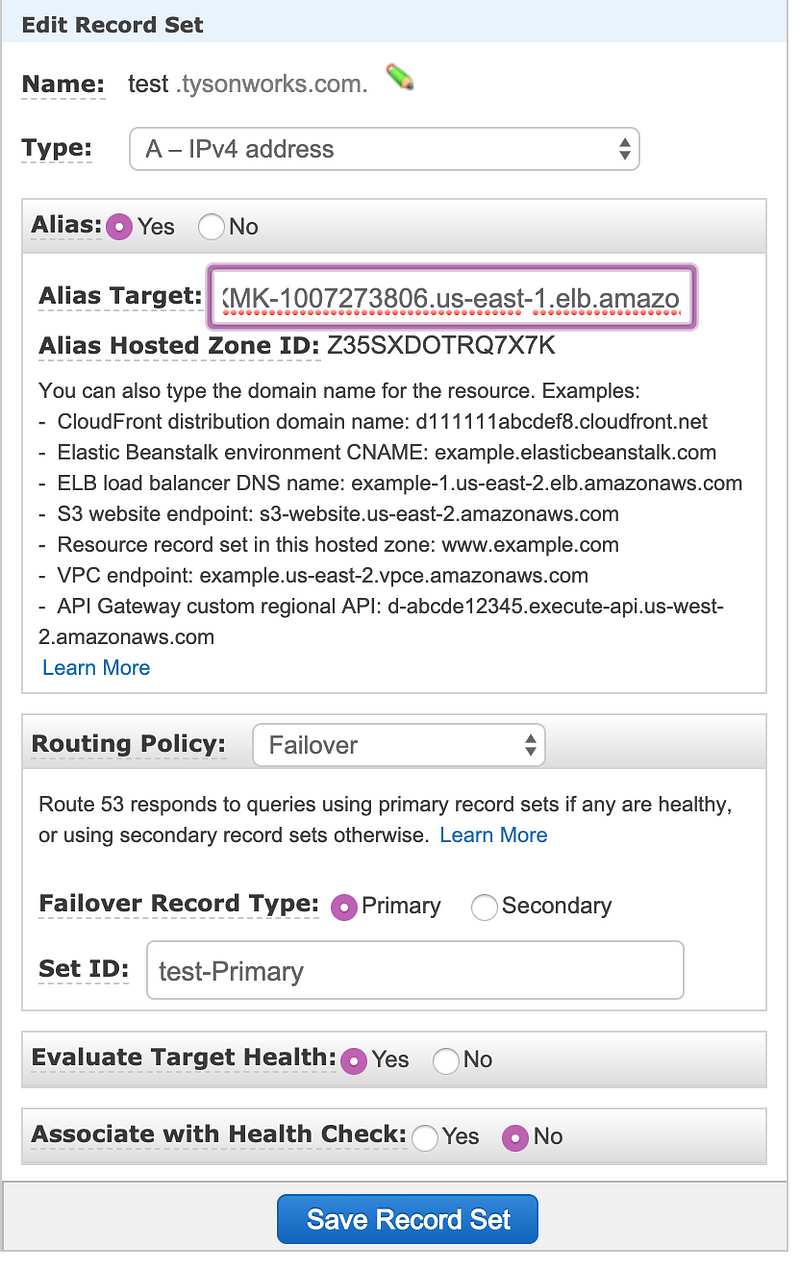
Now set the second record with the ALB in us-west-1 region
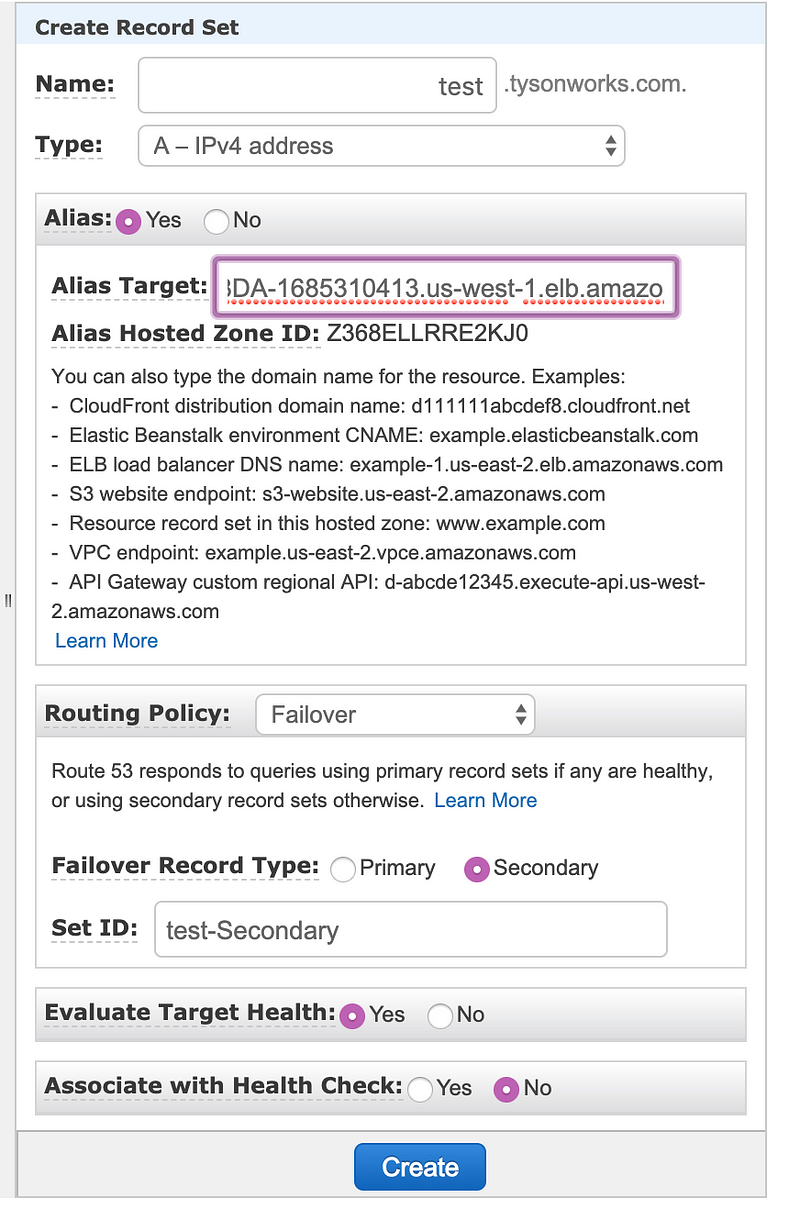
All good. Before we do something, let’s try our domain first.
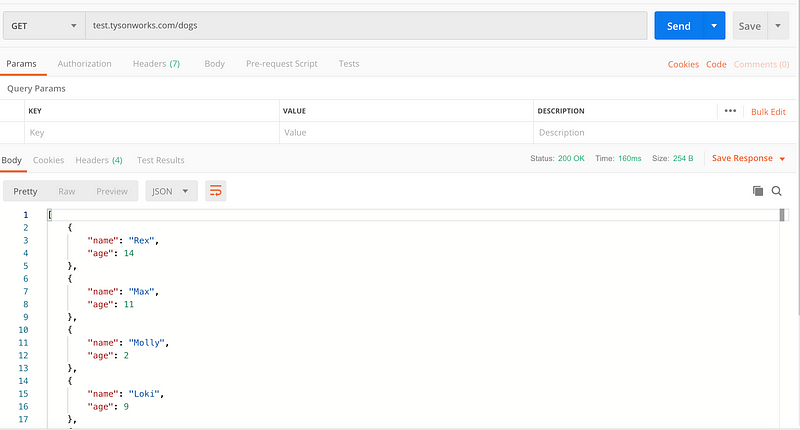
You should be seeing a list of dogs in a JSON response.
Now let’s destroy the first stack, this will remove the resources from the us-east-1 region, which we set as a primary record. But no worries, Route53 will now use a secondary record that we set just earlier.
AWS_REGION="us-east-1" cdk destroy
Let’s make sure that first load balancer is not reachable anymore, which we set as a primary record.

And let’s try our domain again
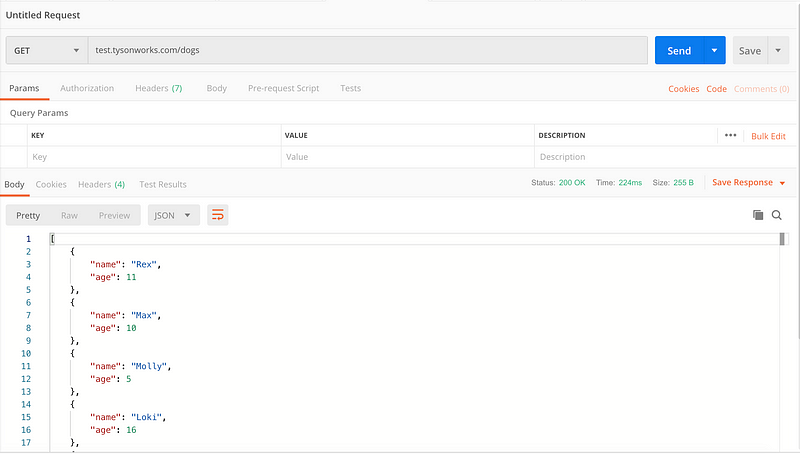
It worked, the secondary target is now serving our requests.
After you are done with the tutorial don’t forget to remove the existing stack we deployed to us-west-1 region.
AWS_REGION="us-west-1" cdk destroy
And delete the A records by selecting each record and then click Delete Record Set in Route53 console.
