Opt Out For AWS Lambda Updates. Why and how?
Opt Out For AWS Lambda Updates. Why and how?

AWS Lambda is a Serverless computing platform that enables users to run code without having to manage servers. It provides a fully managed environment for executing your code, which includes runtime, operating system, and system libraries.
The AWS Lambda execution environment is the environment in which your Lambda function code is executed. It is an isolated environment that has its own resources and dependencies, and it runs on Amazon Linux, a distribution of Linux specifically designed for cloud computing.
AWS Lambda automatically patches the underlying infrastructure for your functions, so you don’t have to worry about managing operating system or runtime updates. This includes security patches for the Amazon Linux operating system, runtime updates for the supported programming languages, and updates to the system libraries that are included in the execution environment.
By default all Lambda functions will get these updates and security patches, but what if you don’t want to do that for specific reasons. What if you want to have more control of the Lambda environment. Well there is a good news if you are looking for that. Few week ago AWS has announced runtime management controls which provide more visibility and control over when Lambda applies runtime updates to your functions. They are also changing how your functions get updated.
Let’s see the new configuration in action.
Head over to the Lambda Console and create a new Function.
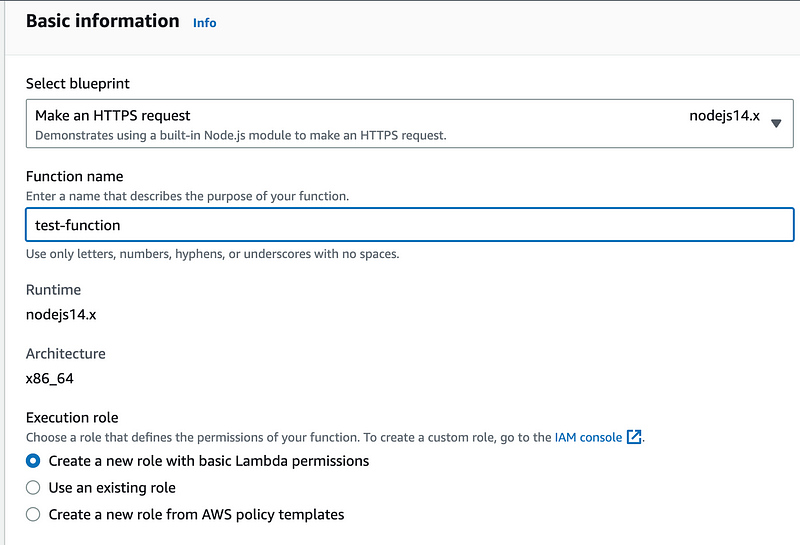
Now that it’s done. Go to the Code tab in your function details page.
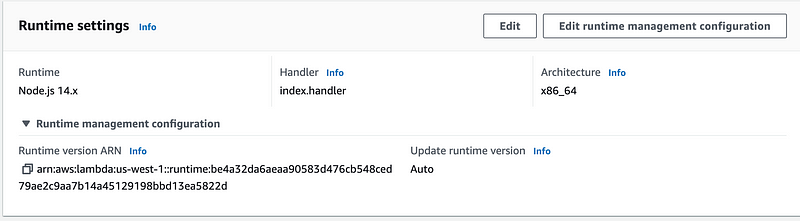
Click Edit runtime management configuration button.
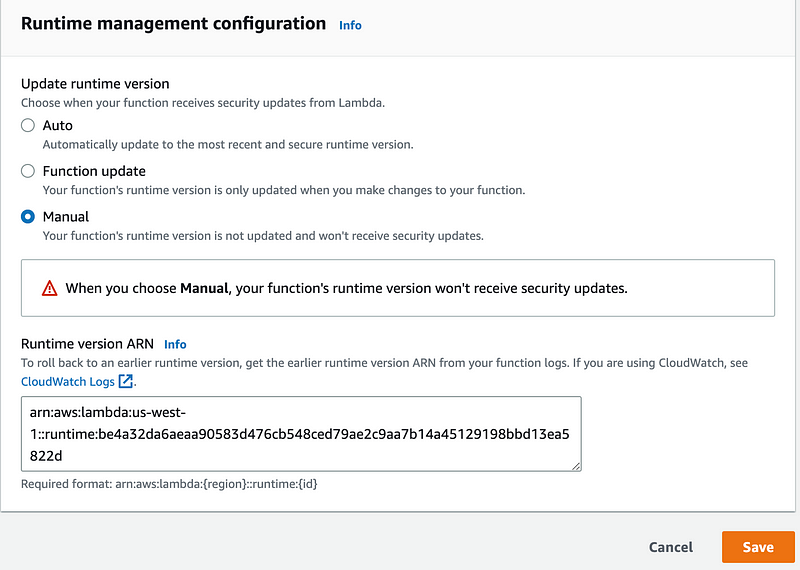
Now we have multiple choices.
- Auto: Your functions will get updates and security patches as usual.
- Function Update: Your function will get updates and security patches only when you update your function code.
- Manual: You won’t get any updates.
The runtime version ARN is a unique identifier for the patching version of a particular runtime. Every time Lambda updates the runtime to apply security and other patches, it creates a new runtime version, with a new ARN.
In conclusion, I don’t recommend opting out of the security updates. But if you have a specific use case for that, you can go ahead and manually manage the updates.
